What is a Work Breakdown Structure?
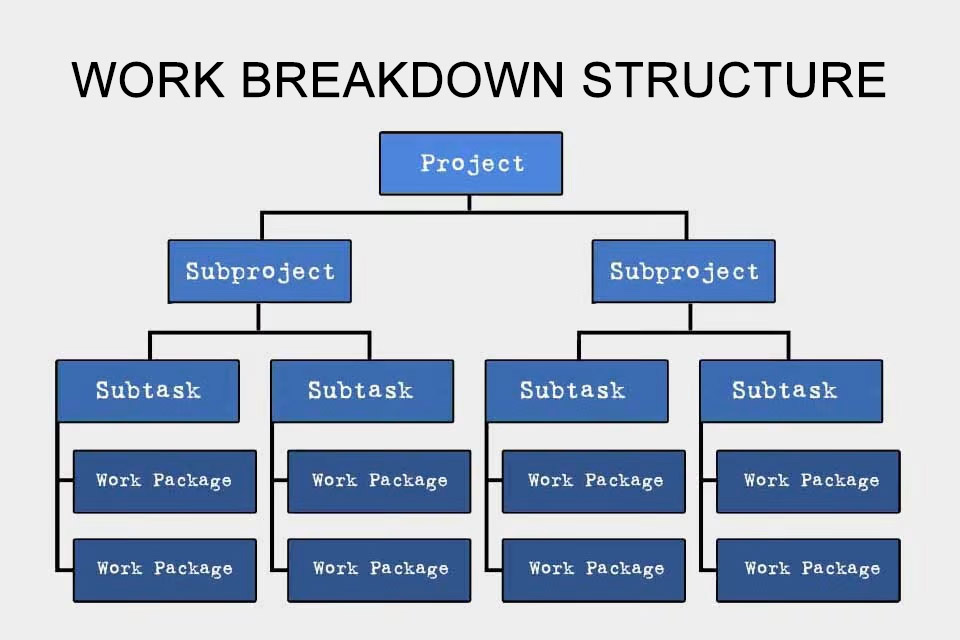
Smartpedia: The work breakdown structure divides a project into subprojects, subtasks and work packages, to which employees, expenses, delivery items, costs and deadlines are assigned.
Work breakdown structure – the hierarchical structure of project work
A work breakdown structure (WBS) hierarchically structures a project by phases, functions or objects with the focus on generating expected results. The Project Management Body of Knowledge Guide (PMBOK), a recognised reference work for project management, defines the work breakdown structure as “a hierarchical structuring of the work to be performed by the project team based on delivery items in order to meet the project objectives and create the required delivery items”.
Put simply, a work breakdown structure says what is to be done in the projects. For this purpose, it divides projects into
- subprojects,
- subtasks and
- work packages
to which employees, expenses, expected delivery items, costs and deadlines are assigned.
Approches to the work breakdown structure
There are three approaches to arranging a work breakdown structure:
- The function-oriented structure uses functional areas such as sales, marketing, development, etc. as structuring elements and defines work packages as activities such as “creating specifications”.
- The object-oriented structure places the results of the project – i.e. components, individual parts or documents such as “systems and software requirement specifications” – at the centre of planning.
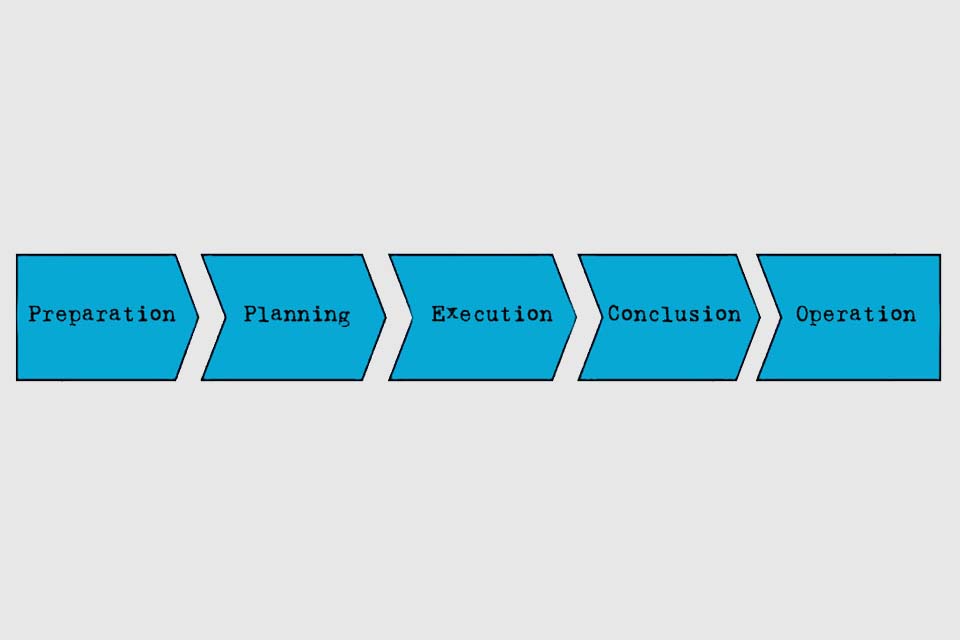
- Phase-oriented structuring uses project phases such as preparation, planning, implementation, etc. for structuring.
In the project practice it frequently comes to mixed forms, whereby it makes sense to use the same outline for subprojects, subtasks and work packages. In this way, subtasks can be object-oriented and work packages function-oriented. The tree structure with many branches or the text structure with a task list, whose entries are indented depending on their structure level, have proven themselves as a form of representation.
Goals and advantages
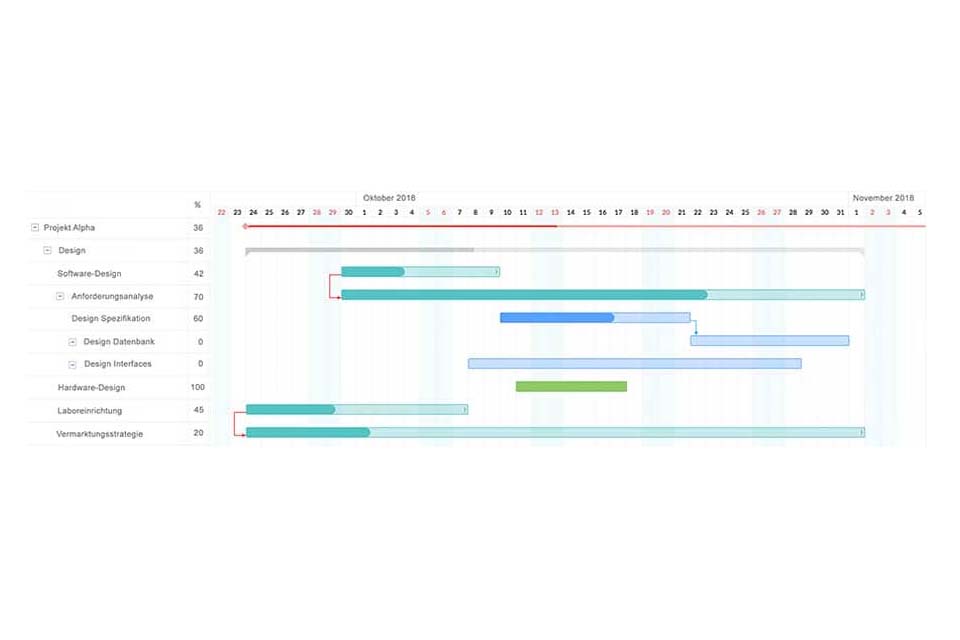
The most important goal of a project structure plan is the complete recording and structuring of all relevant activities of a project. This goal can be achieved through a top-down or bottom-up approach. The top-down approach describes a deductive path from the whole to the detail, i.e. starting with the project and leading to a structure with subprojects, subtasks and work packages. The bottom-up approach is an inductive path – from the work packages to the subtasks and subprojects – and is particularly suitable if the scope of the project cannot yet be determined precisely. In project practice, both approaches are often combined and the work breakdown structure is presented as a Gantt chart.
A work breakdown structure offers the following advantages:
- It is easy to create, easy to understand and provides a good overview of the planned projects.
- It supports the project management in the planning of projects, in particular in scheduling and sequence planning, as well as resource and cost planning. If the WBS is created with a team-capable software solution, the project participants can also profit directly from it, because they receive, for example, information about the work packages they have to process.
- It helps to identify required sub-projects, subtasks or work packages by comparing them with other projects. The use of templates can make sense here.
A work breakdown structure plan is rather unusual for agile projects.
Impulse to discuss
Is it a disadvantage that the work breakdown structure does not make any time-related statements, so that additional process plans or schedules are needed?
Notes:
In some publications, the WBS code is emphasised as the unique identifier of an element within the work breakdown structure. By means of the designation, each element of a project – each risk, each cost rate, each resource, etc. – can be classified or found in the structure of the project. In practice, the WBS code is mainly used in software.
Here you can find a video about the work breakdown structure.
If you like the article or would like to discuss it, please feel free to share it in your network. And if you have any comments, please do not hesitate to send us a message.
Here you will find additional information from our Smartpedia section: