What is the RACI Matrix?
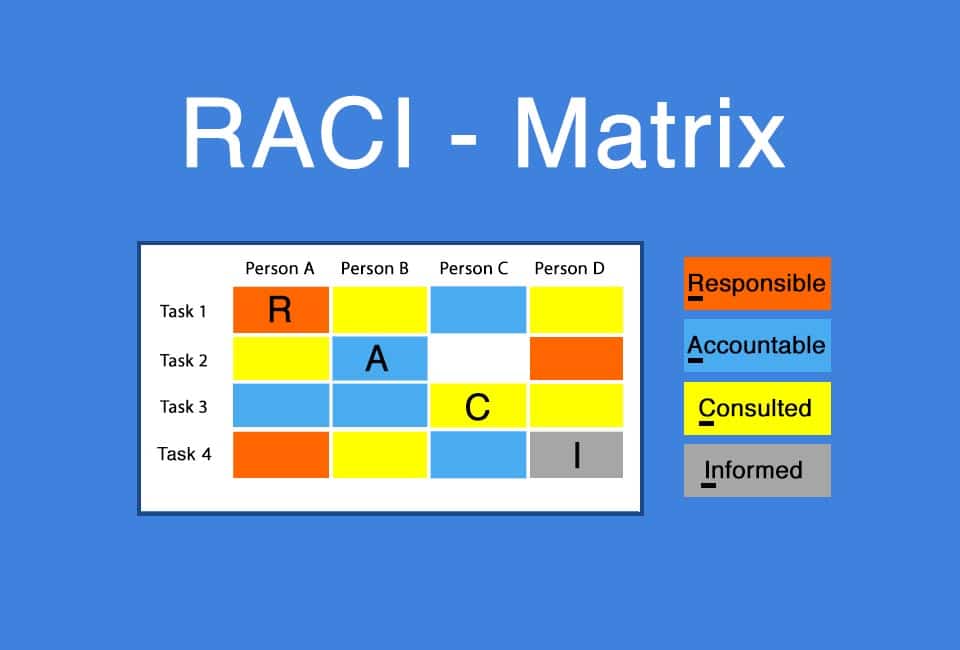
Smartpedia: The RACI matrix is a tool for analysing and presenting responsibilities. RACI is an acronym of the terms Responsible, Accountable, Consulted and Informed.
RACI Matrix – clearly displaying responsibilities
The more stakeholders are involved in a project or development and the more extensive the project or development is, the more difficult it is to define responsibilities and keep track of responsibilities. The RACI matrix – sometimes referred to as the diagram of the same name – is a tool for analysing and presenting responsibilities. RACI is an acronym and stands for
- Responsible
- Accountable
- Consulted
- Informed.
Most often, the activities, work packages, tasks or expected outcomes are represented along the Y-axis, and the staff involved along the X-axis. The representation itself can use a letter assignment, colour coding or a combination of both.
The Interpretation of RACI
These four terms are usually interpreted as follows:
R for Responsible
A role or a specific staff member is responsible for the implementation of an activity; he or she is responsible for the implementation. However, responsible can also mean that the role or the employee “merely” initiates the implementation and the activities are taken over by other roles or employees. In some cases, responsible is also understood as disciplinary responsibility.
A for Accountable
A role or a specific employee is accountable in a commercial and/or legal sense. Accountable often also means that the role or employee approves projects, authorises tasks or signs off on costs and invoices.
C for Consulted
A role or specific employee who should be consulted about an activity because he or she has information, knowledge or experience that is important to the implementation of the activity or realisation of a result.
I for Informed
A role or a specific employee who should be informed about an activity.Here, a distinction can be made between the right to information (the role or employee has the right to information) and the duty to inform (the role or employee must be informed – possibly also cyclically – about activities or results and their progress).
From these different interpretations it can be easily deduced that every organisation using a RACI matrix must reach agreement on the meaning of the terms and the consequences derived from them.
RACI Matrix – Advantages and Disadvantages
The RACI matrix offers some advantages and also has some disadvantages. Here are some advantages:
- The representation is easy to create and understand. If there is agreement on the interpretation of the terms, it is a useful tool for communication design.
- The matrix is not only suitable for visualising responsibilities, but also for defining them. At the same time, it increases mutual understanding of who is responsible for what and who must or should be involved in which activities and how.
- RACI is also very valuable for the definition of interfaces when modelling business processes.
- The representation – as long as everyone is aware of it and it is easily accessible – reduces the potential for conflict due to lack of communication and/or unclear areas of responsibility.
- In many cases, a whiteboard or a wall in the office and some Post-Its are sufficient for the presentation. In addition, there are numerous templates available on the internet, e.g. for MS Excel or MS PowerPoint.
And here you will find some disadvantages and challenges in practice:
- The RACI matrix often appears clear and concise. As the number of activities and participants increases, this clarity often diminishes. If the representation is used on a website, for example, information can often only be accessed by scrolling. In addition, modern websites use a responsive design, so that displays with many columns are not always easy to read.
- The presentation suggests a clear picture of responsibilities. However, in many organisations where, for example, teams work at eye level and through team commitment, this unambiguity does not exist.
- Sometimes it is argued that roles or employees always know which tasks they have to do because of the representation. In everyday business, however, many activities are too small-scale to be visualised accordingly. In addition, roles and employees often participate in activities, i.e. they support the execution and implementation. However, these contributors are not explicitly visualised, so that additional aids or tools are often needed.
- And last but not least, the RACI matrix does not define who informs whom. For example, it specifies who should be informed or consulted, but who provides the information or obtains the relevant information cannot be derived from the visualisation.
Tips on the RACI Matrix
There are a number of tips for using RACI:
Often it is not easy to define “only” one person who is responsible or accountable. So if several people are considered responsible, it might be a good idea to split or divide activities.
The diagram defines four areas of responsibility, in practice there are often more: Contributing employees who are not mentioned in the diagram, stakeholders who may “live” outside the organisational unit, suppliers who are responsible for keeping commitments but have no relation to an internal RACI diagram. These additional roles, staff or institutions still need to be considered in practice.
The RACI matrix is not only a tool for visualising responsibility, but also for analysing it. In the course of the analysis, it is advisable to also think about the provision of information (Status: Informed) or the obtaining of tips (Status: Consulted) and to regulate this accordingly.
It is also advisable to regularly question the use of the diagram. Does the diagram offer the expected benefits? How can the application be improved? Or: perhaps it also makes sense not to use it if the reality of a company cannot be appropriately represented and allocated.
RACI Variants or Alternatives
There are a number of variants or alternatives that take a similar matrix approach but use different terms. Here are some of these variants:
- RASCI: Responsible, Accountable, Support, Consulted, Informed. Support addresses a role or a staff member who assists in an activity and thus supports the implementation. Since the demarcation between S and C is not always easy, there are organisations that give C roles or staff the right of veto.
- RACIO: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed, Omitted. Omitteld explicitly names staff members who have nothing to do with the implementation of a specific activity. Some publications also refer to CAIRO.
- RACI-VS: Responsible, Accountable, Support, Consulted, Informed, Verify, Signatory. Verify designates a role or an employee who verifies a result, e.g. on the basis of defined acceptance criteria. Signatory addresses the confirmation of this verification. Compared to RACI, two additional areas of responsibility are defined.
- REWA: Responsible, Expert, Work, Approver. The Expert corresponds roughly to the “Consulted” of RACI, Work addresses the actual execution of an activity and A stands for Approver and thus for the acceptance of an activity or a result.
In addition, there are several other alternatives that are used in different ways, such as IPCARSED (Initiation, Preparation, Consultation, Approval, Release, Supervision, Execution and Distribution), or in German-speaking countries VIMAF (Verantwortlich, Information, Mitwirkung, Abstimmung, Freigabe), IBZED (Information, Beratung, Zustimmung, Entscheidung und Durchführung) or DEMI (Durchfuehrung, Ergebnis, Mitarbeit und Information). The extent to which these alternatives offer added value compared to RACI should be decided by organisations on a case-by-case basis.
Impulse to discuss
At what quantity of data sets does a RACI diagram become confusing?
Notes:
If you like the article or would like to discuss it, please feel free to share it in your network. And if you have any comments, please do not hesitate to send us a message.
In some publications, the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM) is used as an alternative name to RACI.
Here you can find a PowerPoint template for creating a RACI matrix.
Here you can find instructions in German on how to create a corresponding Excel template.
And here you can find additional information from our Smartpedia Section: