What is Tailoring?
Smartpedia: Tailoring in V-Modell XT describes the static or dynamic process of adapting the process model to system development for a specific project.
Tailoring – cutting the V-Modell XT specifically to size
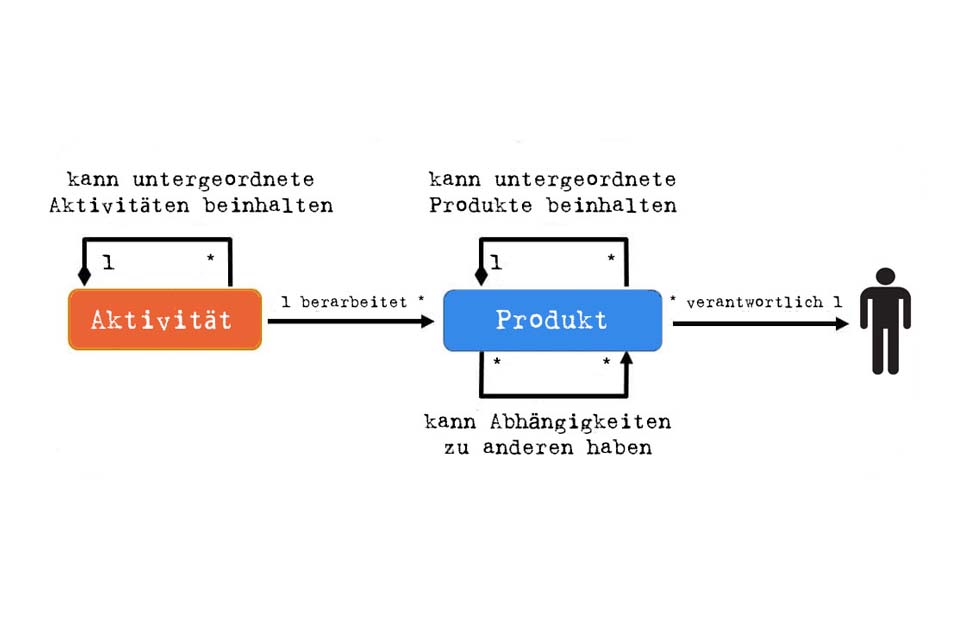
V-Modell XT is a rich process model that can be used for a wide variety of projects. It defines a mechanism for adaptation to a specific project: tailoring. “To tailor” means “to cut” and this is exactly what tailoring is all about: selecting the products and activities that are needed in the specific project and omitting aspects that are not needed.
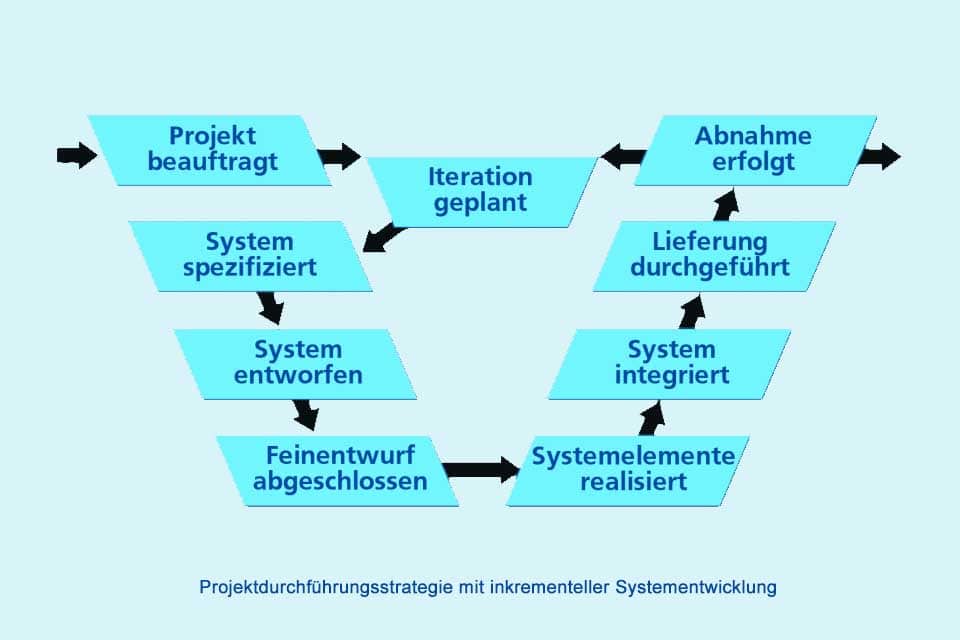
In tailoring, the project type, project type variant and various project characteristics are determined. This results in process modules that encapsulate activities, products and roles, and a project implementation strategy for the chronological arrangement of decision points.
Users need software to tailor V-Modell XT. If it takes place at the beginning of a project, it is referred to as “static tailoring”. Since project characteristics can also change in the course of the project, e.g. if ready-to-use products have to be evaluated after all or a logistics concept has to be created, there is also “dynamic tailoring”. In this case it is important to clarify some questions:
- Did the project execution strategy change and if so, what are the effects on the project plan derived from it? How are decision gates and deadlines changing?
- Will additional products be added or will planned products be omitted? Do already created products have to be revised? Who is in charge of this revision?
- Will new roles be added and if so, who will fill them?
Tailoring itself requires little knowledge of V-Modell XT. The first step is to classify the project, i.e. to determine the project type and the role (client, contractor or both within a common organization). The second step is to select the project type variant and decide whether it is, for example, a development project or an operation and maintenance project. And in the third step, the project characteristics are defined whose quantity has already been reduced by the selection of the project type and the project type variant. The project characteristics are defined by answering questions. For example, the following questions are asked:
- Is the project critical with regard to safety and security?
- Is commercial project planning and tracking necessary?
- Should quantitative project key figures be measured and analyzed?
- Should ready-to-use products be evaluated and used as far as reasonable and possible?
- Should subcontracts be assigned during system development?
- Should an old system be migrated in this project?
- Should prototypes be created during system development?
- …
With tailoring, users lay the foundation for a specific project. The result – depending on the software used – is an initial project plan with project phases including activities and decision points, a product library with templates for the products to be created, and a combination of activities, products, and roles. Further project planning and implementation can begin.
Tailoring as term is also used in the PMBOK Guide.
If you like the article or would like to discuss it, please feel free to share it in your network. And if you have any comments, please do not hesitate to send us a message.
Here you will find additional information from our Smartpedia section: