What is a Decision Table?
Smartpedia: A decision table is a representation for grouped business rules. It defines actions for variant-rich processes.
Decision Table – a representation of situations requiring decisions
A decision table is a compact display format for groups of business or decision rules. A business rule defines which sequence of conditions leads to which sequence of actions. Example: “If a delivery has been accepted by the customer and the invoice has been issued by the contractor, and the payment of the delivery by the customer has not been made by the agreed payment date, then the contractor sends a first reminder to the customer and prepares a possible demand for payment from the customer.
Ideally, business rules are grouped together to ensure that all possible combinations of the conditions used are taken into account and described in a complete, redundant and consistent manner.
The parts of a Decision Table
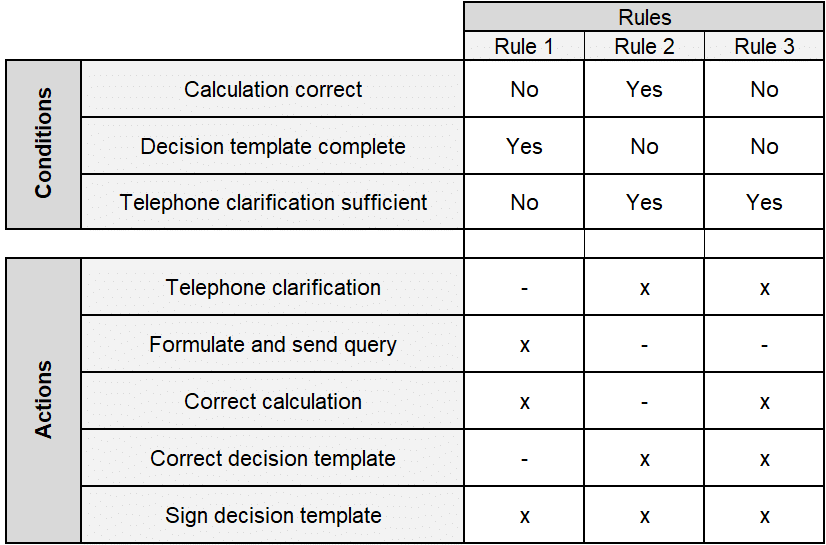
DIN 66241 lists four parts of a decision table:
- The conditions relevant to the decision situation are recorded in the condition part.
- The possible actions are described in the action section.
- The condition display contains the possible combinations of conditions (condition is fulfilled / is not fulfilled / is irrelevant).
- The action display contains the possible actions depending on certain conditions ( execute action / do not execute action).
Notes:
Here you will find additional information from our Smartpedia section: