What is a Cache Miss?
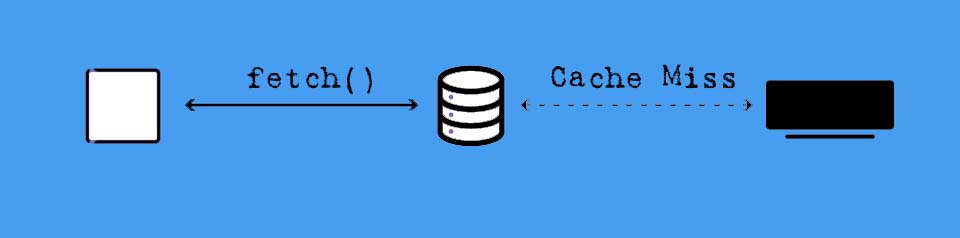
Smartpedia: A cache miss is a state in which requested data is not found in the cache, so that access takes place via subsequent cache levels or the main memory.
ERR_CACHE_MISS
In IT, a cache is a special data memory (e.g. a computer cache, a web cache or a CDN cache) that accelerates (repeated) access to data by temporarily storing it. A cache miss is a state in which the data requested for processing by a component or application is not found in the cache. A cache miss is therefore a miss or failure to access data in the cache.
Reasons for a Cache Miss
There are two basic reasons for a cache miss:
- The requested data is not found in the cache because it was not buffered there.
- The requested data has been cached, but the file attributes have changed since the last cache. Therefore, the data has been removed from the cache.
The result of a cache miss is a latency, since the requested data must be retrieved from the next cache levels or from the main memory. Determining the latency of cache misses is difficult. For example, the same number of errors can cause much greater relative latency in a short-running application than in a long-running application. The size of the cache itself is also important, because the larger a cache is, the more data it can contain, and the more successful accesses it allows.
When considering accesses and errors – the so-called cache miss ratio – a high L1 cache miss ratio may also be acceptable, provided the latency of the L2 cache is low. However, if an L2 cache miss is followed by a prolonged standstill in data access to the main memory, only a low L2 cache miss ratio would be acceptable.
The opposite of a cache miss is a cache hit.
Notes:
Here you will find additional information from our Smartpedia section: