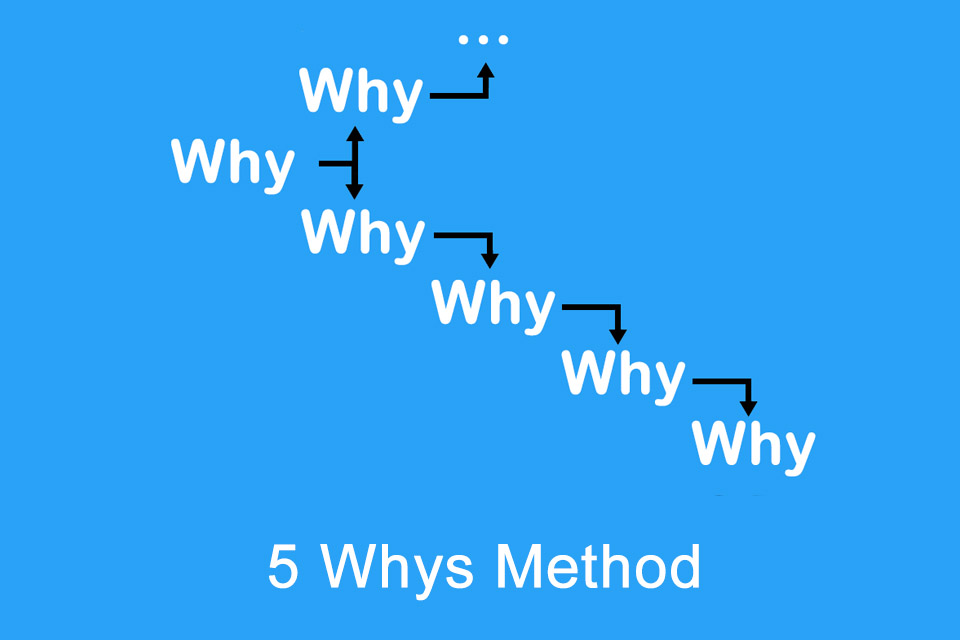
What is the 5 Whys Method?
5 Whys Method – getting to the bottom of causes by asking questions
The question of “why” is often of central importance when assessing situations and problems or when making decisions. “Why” is considered an open-ended question that provides room for detailed answers. But what happens when the answer is not meaningful? Then follow-up questions make sense. And that’s when the 5 Whys Method – also known as 5W, 5 Whys or 5W Method – comes into play. It helps to better understand mistakes and challenges, to examine problems in detail or to understand cause-and-effect relationships.
Interestingly, the 5 Whys Method is considered a central part of the Lean philosophy, an essential tool in root cause analysis or an approach in brainstorming. In fact, it can also be used as a complement to the 5W1H Method or Starbursting.
Toyoda Sakichi¹, a Japanese inventor, is considered the founder of the 5 Whys Method. Among other things, he developed autonomous automation, according to which machines stop automatically when problems occur. This principle was later used at the Toyota Motor Corporation (Toyota), a company founded by Sakichi’s son Toyoda Kiichirō. The aim of the 5 Whys Method is to determine the cause of a problem, with the number 5 merely being an indicator that asking several times (four or six times if necessary) helps to get to the bottom of causes. It follows that the 5W is a root cause analysis tool.
The application of the 5 Whys Method
Below is an example of how to apply it:
Problem: We will not be able to complete project Y on time.
- Why will we not be able to complete the project on time? – Because we have estimated the effort wrongly.
- Why did we estimate the effort wrongly? – Because we did not have all the necessary information at the beginning of the project. And because the client changed his requirements in the course of the project.
- Why did we not have all the necessary information at the beginning of the project? – Because we did not carry out an adequate order clarification.
- Why didn’t we carry out an adequate clarification of the assignment? – Because we did not have the time! And because we believed that we could complete project Y on time without clarifying the mandate.
- Why did we not have time to carry out the order clarification? Because we did not finish project X in time.
This example shows some interesting aspects:
- 5 whys are not always enough to fully clarify a situation.
- Often there are several answers or reasons for a question or problem.
- Each answer to a why determines the next why.
- Even if a cause is identified at the end (in the example: the order clarification that was not carried out), it is not guaranteed that the obvious solution (in the example: carrying out an order clarification) really solves the problem. For example, changing requirements in the project could still lead to delays. Or the order clarification might not work out all the important points for the success of the project. Or…
Advantages and disadvantages of the 5 Whys Method
The 5 Whys Method offers some advantages:
- By asking several times, the cause of a problem can be better understood in detail. A possible solution subsequently addresses this “true” cause and not just a symptom at the top level. At the same time, the solution has a longer-term effect compared to a mere symptom control.
- The application of 5W is flexible; on the one hand, it can be applied to several manifestations of a problem in parallel, on the other hand, it propagates an enquiry only until the real cause of a problem becomes apparent. Moreover, the method can be used for the vast majority of root cause analyses.
- 5W offers the possibility to get rid of assumptions, presumptions or personal perspectives or to question them.
The advantages are counterbalanced by some disadvantages:
- The 5 Whys Method can be used in cause-and-effect relationships. However, in complex situations, in times of uncertainty, there is not always a linear connection between cause and effect. In such situations, asking for reasons often doesn’t lead to suitable answers.
- It often happens that there are several causes for a problem (see example). Although questioning answers may reveal different causes, there is of course no guarantee that all causes will be identified.
- The effect of questioning should not be underestimated. Constant questioning can quickly become counterproductive. Colleagues may react annoyed, superiors may feel attacked and employees may feel underestimated. It may therefore be useful to have a moderator accompany the questioning.
In principle, it is advisable to use the method with caution.
Download the Ideation Whitepaper for free now.
Everything important about Ideation at a glance.
- Definition and tips from practice
- Idea evaluation
- Methods such as reverse and round robin brainstorming, headstand technique, scamper, starbursting, brainwriting, braindumping, Osborn checklist or 1-2-4-All in detail
Knowledge on 17 pages to take away.
Impulse to discuss:
Is there a perceived limit beyond which further enquiry has a negative effect?
Notes:
[1] Toyoda Sakichi
Here you can find a video about The 5 Whys.
In 5 Whys Technique: An Essential Approach for Solving Design Problems in Digital Products you will find some examples of prominent companies using 5 Whys.
Here you will find additional information from the t2informatik Blog: