What is IPMA?
IPMA – an European umbrella organisation for project management
IPMA stands for International Project Management Association and is an umbrella organisation for project management. The IPMA sees itself as an international network for project experts. Like the Project Management Institute (PMI), which was founded as a project management association based in the USA, the IMPA is active worldwide. At present, 70 member associations are active and promote the improvement of project management skills and the exchange between members in their geographical catchment areas.
In Germany the IPMA is supported by the GPM Deutsche Gesellschaft für Projektmanagement e. V., in Austria by Projekt Management Austria (PMA) and in Switzerland by the Swiss Project Management Association (spm). IPMA, which was founded in 1965, is based in the Netherlands.
IPMA Competence Baseline (ICB)
The basics of the competences in project management are laid down in the IPMA Competence Baseline (ICB). The ICB4 has been the current competence standard since 01 July 2018. As the successor to ICB3, which was the basis for the certification system of GPM and IPMA for 13 years, ICB4 defines project, programme and portfolio management as a method and management task in the specific environment.
ICB4 is divided into three areas of competence:
- Perspective (context skills) with 5 elements: strategy (Perspective 1), governance, structures and processes (Perspective 2), compliance, standards and regulations (Perspective 3), power and interests (Perspective 4) and culture and values (Perspective 5).
- People (personal and social competencies) with 10 elements: self-reflection and self-management (People 1), personal integrity and reliability (People 2), personal communication (People 3), relationships and commitment (People 4), leadership (People 5), teamwork (People 6), conflicts and crises (People 7), versatility (People 8), negotiations (People 9) and result orientation (People 10)
- Practice (technical competences) with 14 elements: project, programme or portfolio design (Practice 1), requirements, benefits and objectives (Practice 2), scope of services and delivery objects (Practice 3), procedures and deadlines (Practice 4), organisation, information and documentation (Practice 5), quality (Practice 6), costs and financing (Practice 7), resources (Practice 8), procurement and partnership (Practice 9), planning and control (Practice 10), opportunities and risks (Practice 11), stakeholders (Practice 12), change and transformation (Practice 13) and project selection and portfolio balance (Practice 14).
IPMA certificates
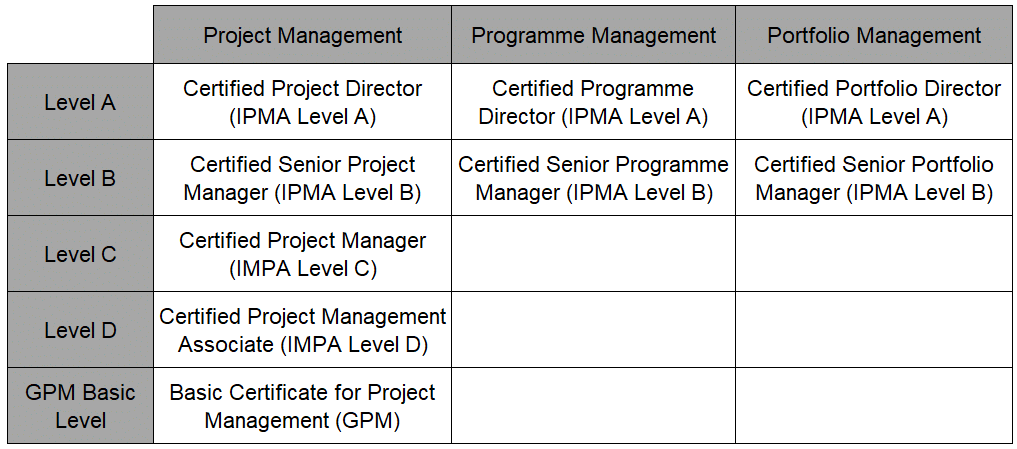
These 29 competencies are reviewed in the course of certifications – another pillar of the IPMA – depending on the level in varying degrees. The distinction between project, programme and portfolio management leads to 9 different certificates:
- The basic level is a certificate for beginners.
- IPMA Level D is also referred to as a knowledge certificate.
- IPMA Level C is the standard certificate for project managers.
- IPMA Level B addresses managers of complex projects.
- IPMA Level A is a certificate for managers of highly complex, strategic projects.
- Every five years, the level achieved is subject to recertification.
Since 2002, IPMA has also been awarding a Project Excellence Award.
Notes:
Further information can be found on the IPMA website or the GPM pages.
If you like the article or would like to discuss it, please feel free to share it in your network. And if you have any comments, please do not hesitate to send us a message.
Here you will find additional information from our Smartpedia section: