What is Conway’s Law?
Smartpedia: Conway’s Law states that the structure of a system to be developed is predetermined by the communication structure of the implementing organisation.
Conway’s Law – the system as a direct result of the organisation
Melvin Edward Conway – a US-American developer – published an article about “How Do Committees Invent” in 1968 in “Datamation”, one of the most famous IT magazines of that time. One of the theses was: “Any organisation that designs a system (defined broadly) will produce a design whose structure is a copy of the organisation’s communication structure.”
Frederick Phillips Brooks Jr. – an American computer and software architect – cited this thesis as “Conway’s Law” in his book “The Mythical Man-Month: Essays on Software Engineering”. Conway’s Law was born.
The foundation for Conway’s Law
Conway’s Law is based on a sociological observation: Only if the developers of module A communicate with the developers of module B in a target-oriented way can modules A and B interact with each other as desired. Or to put it another way: The interaction of the interfaces of a system necessarily depends on the social structure of an organisation. A lack of interpersonal communication leads to a poor solution.
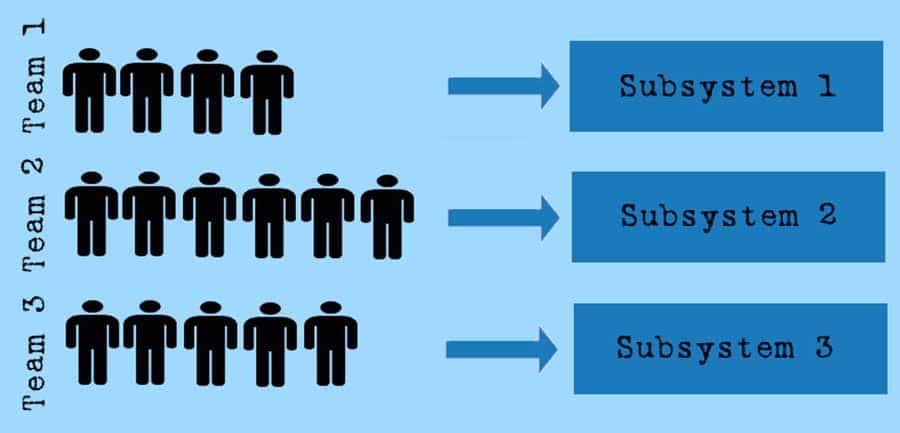
Since 1968, there have been various studies and findings that prove Conway’s Law. What is striking here is that not only the communication between the developers involved is decisive, but also the organisational structure as such. If there are three developer groups E1, E2 and E3, there will usually also be one system with three subsystems S1, S2 and S3, four groups will have four subsystems, etc.
Inverse Conway Manoeuvre as a recommended course of action
In practice, various actions can be observed when dealing with Conway’s Law:
- It is ignored because the participants believe that Melvin Conway’s observation does not apply in the specific case.
- The impact is limited by the parties involved trying to avoid a “collision” of communication patterns and software architecture.
In 2010, Jonny LeRoy and Matt Simons published an alternative recommended course of action: the Invervse Conway Maneuver² (or ICM or Inverse Conway for short). Instead of stopping the regularity, organisations should try to actively use it. This can be done by designing communication and organisational structures to match the desired software architecture. Instead of a frontend and a backend team, there could, for example, be individual functional teams that take care of concrete features that affect both the frontend and the backend.
Impulses to discuss
Since Conway’s Law is not a law or a rigid rule in the true sense of the word, but rather an observation, how well does the term “law” fit in business practice?
And how important is the factor that Melvin Conway formulated his law when the outer limits of software were still called printers and input terminals and not, as today, microservices and cloud computing?
[1] Here you can find the original text of How Do Committes Invent.
[2] In the December issue of the journal Cutter IT, ICM was described as an approach for the first time. (In some publications the approach is also called the Reverse Conway Maneuver).
[3] Adapting the communication and organisational structure may sound simple, but in practice it is often not so easy to implement, especially as the consequences should be well thought through. In some organisations, for example, the existing power and social dynamics can make it difficult to implement change. Those who have power and influence in the current organisational structure may resist if their positions or authority are challenged. This can lead to key stakeholders blocking or sabotaging restructuring, even if it makes sense for technical or organisational reasons. In addition, organisations often have “historical commitments” and thus a lot of legacy in the form of software, systems and organisational structures. Making appropriate changes here is often associated with considerable costs and risks.
If you like the article or would like to discuss it, please feel free to share it in your network. And if you have any comments, please do not hesitate to send us a message.
Here you can find additional information from our t2informatik Blog: